3.4.4 Nomenclature and Isomerism in Organic Chemistry - Naming organic compounds
Students should:
|
Homologous series and functional groups
An homologous series is a family of compounds that all contain the same functional group(s) and differ in successive members by one -CH2- unit.
The following is a list of the common groups:
| homologous series | functional group | description |
| alkanes | Default (no functional group) | only carbons, hydrogens and single bonds |
| alkenes | C=C | 1 double bond, unsaturated |
| alkynes | C |
1 triple bond |
| alcohols | -OH | hydroxy or alcohol group |
| halogenoalkanes | -Cl, -Br, -I | one halogen atom attached to chain |
| aldehydes | -CHO | terminates a chain with a carbonyl group and hydrogen |
| ketones | -CO- | carbonyl group in the middle of a chain |
| carboxylic acids | -COOH | terminates a chain with a carbonyl and a hydroxyl group |
| acid chlorides | -COCl | terminates a chain with a carbonyl and chlorine |
| nitriles | -C |
terminates a chain with a triple bond N |
| amines | -NH2 | may be 1º, 2º or 3º |
| amides | -CONH2 | carbonyl and amine groups |
| ethers | R-O-R | alkyl groups bridged by oxygen |
| esters | RCOOR | alkyl groups linked by -COO- |
Nomenclature
Compounds should be named using a rigorous system.
- 1 Identify the root
- 2 Prioritise the functional groups and obtain the suffix to the root
- 3 Add in other functional group and branches including locants if needed as prefixes
The root of the name comes from the number of carbons in the longest chain, unless there is a terminating group or a multiple bond on one of the chains in which case this becomes the root.
- 1 carbon chain = meth-
- 2 carbon chain = eth-
- 3 carbon chain = prop-
- 4 carbon chain = but-
- 5 carbon chain = pent-
- 6 carbon chain = hex-
Functional group priority and names
The group with the most oxidised carbon takes priority in case of competition. The functional group usually gives the suffix to the root. However, in the case of halogens these become a prefix.
| group | suffix |
| alkene | -ene |
| alkyne | -yne |
| alcohol | -anol |
| aldehyde | -anal |
| ketone | -anone |
| nitrile | -anonitrile |
| carboxylic acid | -anoic acid |
| acid chloride | -anoyl chloride |
| amine | -ylamine |
| amide | -anamide |
| esters | (alkyl) -anoate |
| ethers | -oxy(alkane) |
|
|
|
| prefix | |
| haloalkane | chloro-, bromo-, iodo- |
| alkyl branch | alkyl- |
Locants (positioning numbers)
These are numbers that are used with branches or functional groups to avoid ambiguity. They are placed in front of the part of the name to which they refer, separated by a dash.
For example, propanol. The name does not tell us whereabouts in the structure the -OH group is located. A locant is needed, which is placed in the suffix of the name, indicating alcohol, propan-1-ol, or propan-2-ol
 |
 |
| propan-1-ol | propan-2-ol |
The locants are always numbered from the end of the chain that produces the lowest numbers.
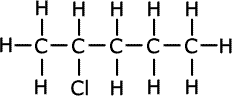 |
| 2-chloropentane |
A locant is used for every attached heteroatom or group.
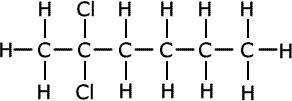 |
| 2,2-dichlorohexane |
Aromatic chemistry
This deals with the chemistry of benzene and its compounds. The benzene ring is a hexagon of six carbon atoms each of which is attached to a hydrogen atom. There are the equivalent of three double bonds within the ring, their electrons delocalised around the ring. This is drawn in shorthand form as a hexagon with a ring inside.
.gif) |
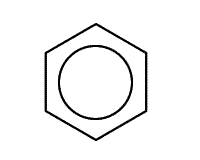 |
| Benzene showing atoms and bonds | representation of benzene |
Naming aromatic systems
The benzene ring may take one of two names in its compounds, a suffix or a prefix:
- -benzene
- Phenyl- or phen-
There is no logical way to ascertain which is used and often both are acceptable. It's just a matter of learning the different structures.
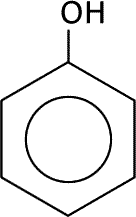 |
 |
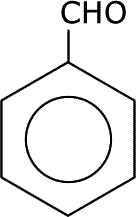 |
| phenol | phenylamine or aminobenzene | benzaldehyde |
There are many more trivial names still associated with aromatic systems and these are in common use, particularly in research establishmetns and industry. For instance, phenylamine (above) is usually called aniline. Methylbenzene is called toluene, etc..
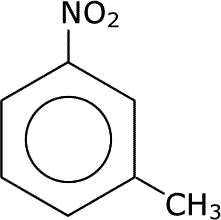
Where there are two (or more) substituents attached to the benzene ring, the substituent with the highest priority (most oxidised group) is assigned position 1 on the ring and the ring carbons are then numbered clockwise.
 |
 |
 |
| 2-nitromethylbenzene | 3-nitromethylbenzene | 2,4,6-trinitromethylbenzene (TNT) |
NOTE The initials TNT come from the old (trivial) name for methylbenzene, toluene.