3.4.8 Amino Acids - Acid and base properties
Students should:
|
Formation of ions by amino acids
Amino acids have both acidic carboxylic acid groups and basic amine groups of atoms.
The amine group of atoms has a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen which can accept a hydrogen ion. It consequently behaves as a base.
R-NH2 + H+ R-NH2+
The carboxylic acid group can lose a hydrogen ion and behave as an acid.
R-COOH  R-COO- + H+
R-COO- + H+
The actual species present at any one time depends on the pH of the medium in which the species is located.
If the solvent is basic, the hydrogen ions tend to be removed from the carboxylic acid group, forming a negative ion. If the medium is acidic, there is a tendency for the nitrogen of the amine to accept a hydrogen ion and become a positive ion.
Both of these acid-base type reactions are equilibria. As the pH decreases, the equilibrium of the carboxylic acid group moves more to the side of the -COOH, while the amine equilibrium moves more to the side of the -NH3+.
Logically, there must be some pH, intermediate between the two extremes, at which the tendency to form a negative ion is the same as the tendency to form a positive ion.
Isoelectric point
If charged particles are free to move and are in the presence of an electrical field, negatively charged particles travel towards the positive potential and positively charged particles travel towards the negative potential.
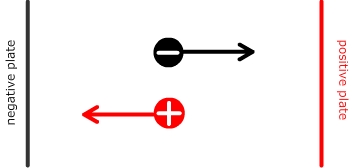
An amino acid which has an equal amount of both positive and negative charge at a a specific pH is said to be at the isoelectric point. When an electrical potential is applied across the species at this pH there will be equal pull in both directions and the species will not be able to move.
Isoelectric point = the situation that arises when the charges on the amino acid balance and there is no overall force in any direction under the influence of an electrical field.

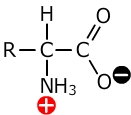
Zwitterion
The name 'zwitterion' comes from the German 'zwei' meaning two. Hence, a zwitterion is a species that contains both a positive and a negative charge. Amino acids tend to form positive ions at high pH and negative ions at low pH.
When they are within the appropriate pH range to form both ions simultaneously this is called the zwitterion.