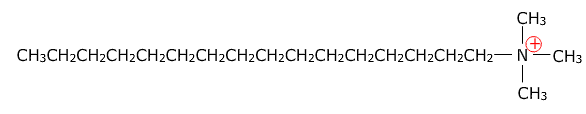3.4.7 Amines - Nucleophilic properties
Students should:
|
Nucleophilic substitution of haloalkanes using ammonia
Ammonia reacts with haloalkanes by nucleophilic substitution to form amines.

The reaction can proceed further as the product also reacts with ammonia making secondary and then tertiary amines.
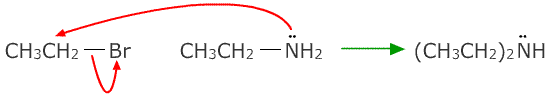
Even tertiary amines can react with haloalkanes forming quaternary salts:
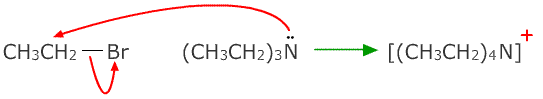
Cationic surfactants
Surfactants are compounds that lower the surface tension of a liquid, or that between a liquid and a solid. Surfactants may act as detergents, wetting agents, emulsifiers, foaming agents, and dispersants.
A cationic surfactant is a structure with a positive charge. For a quaternary ammonium salt to act as a cationic surfactant, one of the alkyl groups is typically much larger than the other three. For example, cetrimonium bromide, (hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide, CTAB, ((C16H33)N(CH3)3Br).
Cetrimonium ion