3.4.6 Aromatic Chemistry - Nitration
Students should:
|
Nitration of benzene
Nitration is a very important reaction as it adds a nitro- group to an aromatic ring. This in turn may be converted into an amine group. Nitrated aromatic compounds have many uses in industry, particularly in explosives, drugs and medicines and dyestuffs.
Explosives
The discovery of 2,4,6-trinitromethylbenzene (TNT) was the first step in the development of high explosives. TNT, from the old name trinitrotoluene, is the result of nitrating a benzene ring which already has a methyl group attached. Each nitro- group deactivates the aromatic ring, making is more difficult to substitute the second and third nitro- groups.
For example, in the nitration of benzene:

The conditions required are relatively mild, but to introduce the second and third nitro group more time and heat are required.
Reduction of nitrobenzene
The nitro group is easily reduced by a mixture of tin and hydrochloric acid

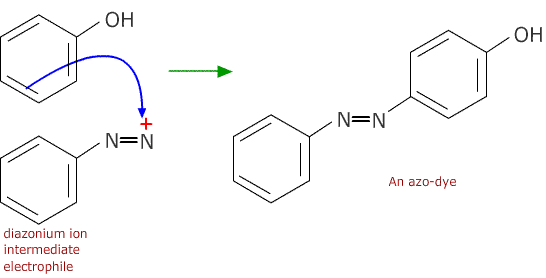
The product, phenylamine, also called aminobenzene or aniline, is an important intermediate in the production of azo dyes.
The first stage is to produce a diazonium ion intermediate by reacting phenylamine with nitrous acid below 5ºC
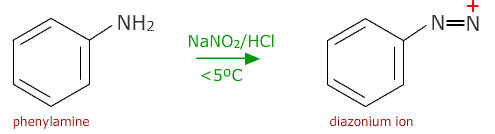
The second stage is reaction of the diazonium ion with a phenol to make the azo dye: